Agentic AI Framework
Overview
The Agentic AI Framework is a composable enterprise framework for building intelligent AI agents with Amazon Bedrock that can be mixed and matched across diverse use cases - from document processing and conversational AI to data analysis and automated decision-making workflows.
Build sophisticated AI agents that go beyond simple text generation using this modular framework from AppMod Catalog Blueprints. Create intelligent agents for any use case by mixing and matching reusable components across different business domains and industries.
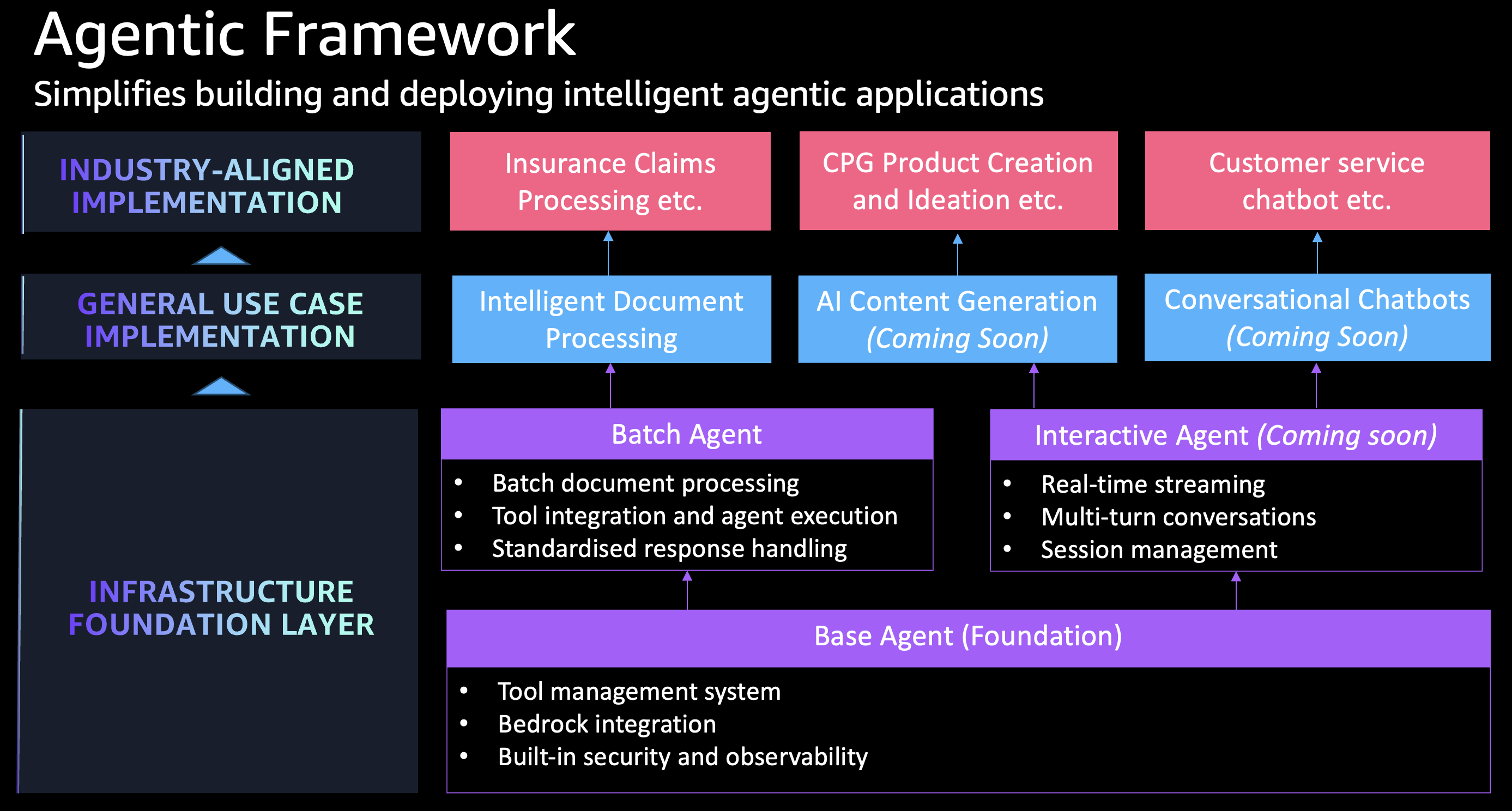
You can leverage the following constructs:
- BaseAgent: Abstract foundation requiring custom agent implementations
- BatchAgent: Ready-to-use agent for batch processing with Bedrock integration
- InteractiveAgent: Real-time conversational AI with SSE streaming, session management, and Cognito authentication
All implementations share common infrastructure from BaseAgent and integrate with the Strands agent framework for tool execution and model interaction.
Composable Architecture
Mix & Match Components
- BaseAgent: Foundation infrastructure that works across all use cases
- BatchAgent: Ready-to-use for document processing, data analysis, content generation
- InteractiveAgent: Ready-to-use for chatbots, customer service, real-time conversations
- Tool Library: Reusable capabilities that work across different agent types
Multi-Use Case Support
The same framework components power diverse applications:
- Insurance Claims: Document classification → data extraction → validation → approval workflows
- Customer Service: Query understanding → knowledge retrieval → response generation → escalation handling
- Content Operations: Research → writing → fact-checking → publishing workflows
- Data Analytics: Data ingestion → analysis → insight generation → report creation
- Manufacturing: Quality control → defect analysis → predictive maintenance → process optimization
Composability Benefits
- Reusable Infrastructure: Deploy the same BaseAgent foundation across all your AI initiatives with consistent security, monitoring, and compliance
- Flexible Scaling: Start with BatchAgent for immediate value, add InteractiveAgent for customer-facing applications, combine multiple agents for complex workflows
- Rapid Customization: Swap AI models based on use case requirements, modify prompts and workflows without changing infrastructure, add new tools as business needs evolve
Components
The following are the key components of this L3 Construct:
Agent Definition
The agent definition encapsulates the core configuration that influences agent behavior:
interface AgentDefinitionProps {
// Bedrock model configuration
readonly bedrockModel: BedrockModelProps;
// System prompt stored as S3 asset
readonly systemPrompt: Asset;
// Optional tools for agent capabilities
readonly tools?: Asset[];
// Dependencies for tools
readonly lambdaLayers?: LayerVersion[];
// Additional IAM permissions for tools
readonly additionalPolicyStatementsForTools?: PolicyStatement[];
}
Tool Integration
Agents can be enhanced with custom tools stored as Python files in S3:
const tools = [
new Asset(this, 'DownloadPolicyTool', {
path: './tools/download_policy.py'
}),
new Asset(this, 'DataAnalysisTool', {
path: './tools/data_analysis.py'
})
];
Tools are automatically loaded by the agent runtime and can include:
- File processing utilities
- API integrations
- Data analysis functions
- Specialized domain logic
Infrastructure Features
- Encryption: KMS encryption for environment variables and data at rest
- Networking: Optional VPC deployment with subnet selection
- Observability: AWS Lambda Powertools integration for metrics, tracing, and logging
- IAM Security: Least-privilege access with automatic permission generation
- Scalability: Configurable memory allocation and timeout settings
BaseAgent Construct
The BaseAgent construct is the foundational abstract class for all agent implementations. It provides complete serverless agent infrastructure and takes care of the following:
- Initializes IAM roles with appropriate permissions for Bedrock and tools
- Configures KMS encryption for secure environment variable storage
- Sets up observability with Lambda Powertools integration
- Manages tool asset permissions and S3 access
- Provides VPC networking support when required
Implementation Requirements
If you're directly extending this abstract class, you must provide concrete implementations of:
agentFunction: The Lambda function that executes the agent logic
Configuration Options
- Agent Name: Unique identifier for the agent
- Agent Definition: Core configuration including model, prompts, and tools
- Network: Optional VPC deployment with subnet selection
- Encryption Key: Custom KMS key or auto-generated
- Observability: Enable logging, tracing, and metrics
- Removal Policy: Resource cleanup behavior (default: DESTROY)
BatchAgent Construct
The BatchAgent construct extends BaseAgent and provides a ready-to-use implementation for batch processing scenarios.
Key Features
- Inherits: All base infrastructure (IAM, KMS, observability)
- Implements: Complete Lambda function with Strands agent framework
- Adds: Batch processing capabilities with configurable prompts
- Includes: JSON extraction and response formatting
Configuration Options
You can customize the following:
- Prompt: Processing instructions for the agent
- Expect JSON: Enable automatic JSON extraction from responses
- Memory Size: Lambda memory allocation (default: 1024MB)
- Timeout: Execution timeout (default: 10 minutes)
- Architecture: Lambda architecture (default: X86_64)
Example Usage
import { BatchAgent } from '@cdklabs/cdk-appmod-catalog-blueprints';
import { Asset } from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-s3-assets';
const agent = new BatchAgent(this, 'DocumentAnalysisAgent', {
agentName: 'DocumentAnalysisAgent',
agentDefinition: {
bedrockModel: {
useCrossRegionInference: true
},
systemPrompt: new Asset(this, 'SystemPrompt', {
path: './prompts/document_analysis.txt'
}),
tools: [
new Asset(this, 'PDFTool', {
path: './tools/pdf_processor.py'
}),
new Asset(this, 'OCRTool', {
path: './tools/ocr_processor.py'
})
]
},
prompt: `
Analyze the provided document and extract key information.
Use the available tools to process different document formats.
Return results in JSON format with extracted data and confidence scores.
`,
expectJson: true,
enableObservability: true
});
Tool Development
Tools are Python files that extend agent capabilities:
# tools/pdf_processor.py
from strands import tool
@tool
def extract_pdf_text(file_path: str) -> str:
"""Extract text content from PDF files."""
# Implementation here
return extracted_text
@tool
def get_pdf_metadata(file_path: str) -> dict:
"""Extract metadata from PDF files."""
# Implementation here
return metadata
Event Payload Structure
The agent expects input in the following format:
{
"contentType": "file",
"content": {
"bucket": "my-bucket",
"key": "documents/report.pdf",
"location": "s3"
},
"classificationResult": {
"documentClassification": "compliance_report"
}
}
Response Format
With expectJson: true, responses are automatically parsed:
{
"result": {
"compliance_status": "compliant",
"issues_found": [],
"confidence_score": 0.95,
"recommendations": [
"Review section 3.2 for clarity"
]
}
}
InteractiveAgent Construct
The InteractiveAgent construct extends BaseAgent to provide real-time conversational AI with SSE streaming, session management, and authentication.
Key Features
- Inherits: All base infrastructure (IAM role, KMS encryption, tool management, observability)
- Implements: Lambda function with Lambda Web Adapter + FastAPI for Python response streaming
- Adds: API Gateway REST API with response streaming, S3 session management, sliding window context, Cognito authentication
- Strategy Interfaces: Pluggable adapters for communication, sessions, context, and authentication
Architecture
Client (fetch + ReadableStream)
↓ POST /chat (Authorization: Bearer JWT)
API Gateway REST API (responseTransferMode: STREAM)
↓ InvokeWithResponseStream
Lambda (Python + Lambda Web Adapter + FastAPI)
↓ strands.Agent streaming
Amazon Bedrock (Claude)
The Lambda function runs a FastAPI application behind Lambda Web Adapter. When a chat request arrives:
- API Gateway validates the JWT via native Cognito authorizer
- API Gateway invokes Lambda using
InvokeWithResponseStream - Lambda Web Adapter forwards the HTTP request to FastAPI on
localhost:8080 - FastAPI loads session history from S3, applies context windowing, creates a
strands.Agent, and streams SSE events as the agent generates tokens - SSE chunks stream back through Lambda Web Adapter → API Gateway → Client
Components
StreamingHttpAdapter (Default Communication Adapter)
Creates an API Gateway REST API with response streaming enabled. Supports 15-minute timeout, native Cognito JWT validation, CORS, and configurable throttling.
const adapter = new StreamingHttpAdapter({
stageName: 'prod',
throttle: { rateLimit: 100, burstLimit: 200 },
});
S3SessionManager (Default Session Store)
Persists conversation state to S3 with automatic expiration via lifecycle policies. Each HTTP request loads/saves session state, enabling multi-turn conversations over stateless HTTP.
const sessionStore = new S3SessionManager(this, 'SessionStore', {
sessionTTL: Duration.hours(48),
encryptionKey: myKmsKey,
});
SlidingWindowConversationManager (Default Context Strategy)
Maintains a fixed-size window of recent messages, automatically discarding older messages. Configurable window size (default: 20 messages).
const contextStrategy = new SlidingWindowConversationManager({ windowSize: 50 });
NullConversationManager
Disables conversation history. Each message is processed independently.
CognitoAuthenticator (Default Authenticator)
Integrates with Amazon Cognito User Pools. API Gateway validates JWT tokens natively using the COGNITO_USER_POOLS authorizer type — no custom Lambda authorizer needed.
const authenticator = new CognitoAuthenticator({
removalPolicy: RemovalPolicy.RETAIN,
});
NoAuthenticator
Disables authentication entirely. Only use for development and testing.
Configuration Options
| Property | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
communicationAdapter | ICommunicationAdapter | StreamingHttpAdapter | Communication mechanism |
sessionStore | ISessionStore | S3SessionManager | Session persistence (undefined for stateless) |
sessionBucket | IBucket | Auto-created | Custom S3 bucket for sessions |
sessionTTL | Duration | 24 hours | Session expiration time |
contextStrategy | IContextStrategy | SlidingWindow size 20 | Context management strategy |
messageHistoryLimit | number | 20 | Max messages in context window |
authenticator | IAuthenticator | CognitoAuthenticator | Authentication mechanism |
memorySize | number | 1024 MB | Lambda memory allocation |
timeout | Duration | 15 minutes | Lambda timeout |
architecture | Architecture | X86_64 | Lambda architecture |
reservedConcurrentExecutions | number | undefined | Reserved Lambda concurrency |
All BaseAgentProps | — | — | Inherited from BaseAgent |
Outputs
agent.apiEndpoint; // REST API endpoint URL (POST /chat)
agent.adapter; // ICommunicationAdapter instance
agent.sessionStore; // ISessionStore instance
agent.sessionBucket; // S3 bucket for sessions
agent.contextStrategy; // IContextStrategy instance
agent.authenticator; // IAuthenticator instance (access userPool, userPoolClient)
agent.agentFunction; // Lambda function
agent.agentRole; // IAM role (inherited from BaseAgent)
agent.encryptionKey; // KMS key (inherited from BaseAgent)
Usage Examples
Minimal Configuration
import { Asset } from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-s3-assets';
import { InteractiveAgent } from '@cdklabs/cdk-appmod-catalog-blueprints';
const systemPrompt = new Asset(this, 'SystemPrompt', {
path: './prompts/chatbot_system_prompt.txt',
});
const agent = new InteractiveAgent(this, 'ChatAgent', {
agentName: 'CustomerSupportBot',
agentDefinition: {
bedrockModel: { useCrossRegionInference: true },
systemPrompt,
},
});
// REST API endpoint for client connections
console.log('API Endpoint:', agent.apiEndpoint);
Full Configuration
const agent = new InteractiveAgent(this, 'ChatAgent', {
agentName: 'CustomerSupportBot',
agentDefinition: {
bedrockModel: {
fmModelId: FoundationModelIdentifier.ANTHROPIC_CLAUDE_3_HAIKU_20240307_V1_0,
},
systemPrompt,
tools: [
new Asset(this, 'KBTool', { path: './tools/knowledge_base_search.py' }),
],
},
communicationAdapter: new StreamingHttpAdapter({
stageName: 'prod',
throttle: { rateLimit: 1000, burstLimit: 2000 },
}),
sessionTTL: Duration.hours(24),
contextStrategy: new SlidingWindowConversationManager({ windowSize: 50 }),
authenticator: new CognitoAuthenticator(),
memorySize: 2048,
timeout: Duration.minutes(15),
enableObservability: true,
metricNamespace: 'my-app',
metricServiceName: 'chatbot',
});
SSE Event Format
event: metadata
data: {"session_id": "uuid-string"}
data: {"text": "Hello"}
data: {"text": ", how can I help?"}
event: done
data: {}
Example Implementations
- Customer Support Chatbot — Full-stack chatbot with React frontend, Cognito auth, and SSE streaming
Knowledge Base Integration
Agents can be enhanced with knowledge base capabilities for Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). This enables agents to query configured knowledge bases during task execution, retrieving relevant context to improve response quality.
Basic Knowledge Base Configuration
import { BedrockKnowledgeBase, BatchAgent } from '@cdklabs/cdk-appmod-catalog-blueprints';
// Create knowledge base reference
const productDocs = new BedrockKnowledgeBase(this, 'ProductDocs', {
name: 'product-documentation',
description: 'Product documentation and FAQs. Use for product feature questions.',
knowledgeBaseId: 'ABCD1234',
});
// Create agent with knowledge base
const agent = new BatchAgent(this, 'SupportAgent', {
agentName: 'CustomerSupportAgent',
agentDefinition: {
bedrockModel: { useCrossRegionInference: true },
systemPrompt: new Asset(this, 'SystemPrompt', {
path: './prompts/support_agent.txt'
}),
knowledgeBases: [productDocs],
},
prompt: 'Answer the customer question using available knowledge bases.',
enableObservability: true,
});
Multiple Knowledge Bases
Configure multiple knowledge bases for different information sources:
const productDocs = new BedrockKnowledgeBase(this, 'ProductDocs', {
name: 'product-docs',
description: 'Product documentation and user guides',
knowledgeBaseId: 'KB_PRODUCT',
});
const policyDocs = new BedrockKnowledgeBase(this, 'PolicyDocs', {
name: 'policy-docs',
description: 'Company policies and compliance documents',
knowledgeBaseId: 'KB_POLICY',
});
const agent = new BatchAgent(this, 'Agent', {
agentDefinition: {
knowledgeBases: [productDocs, policyDocs],
// ... other props
},
});
Retrieval Tool Usage
When knowledge bases are configured, a retrieve_from_knowledge_base tool is automatically available to the agent:
# The agent can call this tool automatically
retrieve_from_knowledge_base(
query="How do I reset my password?",
knowledge_base_id="product-docs" # Optional: query specific KB
)
The tool returns structured results:
{
"success": true,
"results": [
{
"content": "To reset your password, navigate to Settings > Security...",
"source": { "type": "s3", "uri": "s3://docs/password-guide.pdf" },
"score": 0.95,
"knowledgeBaseName": "product-docs"
}
],
"metadata": {
"totalResults": 5,
"queryLatencyMs": 234,
"knowledgeBasesQueried": ["KB_PRODUCT"]
}
}
Advanced Configuration
const kb = new BedrockKnowledgeBase(this, 'AdvancedKB', {
name: 'secure-docs',
description: 'Sensitive documentation with access control',
knowledgeBaseId: 'KB_SECURE',
retrieval: {
numberOfResults: 10, // Return more results (default: 5)
},
acl: {
enabled: true, // Enable identity-aware filtering
metadataField: 'team' // Filter by team metadata
},
guardrail: {
guardrailId: 'my-guardrail',
guardrailVersion: '1'
},
});
For detailed documentation on knowledge base configuration, ACL, guardrails, and custom implementations, see the Knowledge Base README.
Security & Best Practices
IAM Permissions
- Agents automatically receive least-privilege access to required services
- Bedrock model permissions are generated based on model configuration
- Tool-specific permissions can be added via
additionalPolicyStatementsForTools - S3 access is granted only to tool assets and required buckets
Encryption
- Environment variables are encrypted using KMS
- Custom encryption keys can be provided or auto-generated
- Tool assets are encrypted at rest in S3
Observability
- AWS Lambda Powertools integration for structured logging
- X-Ray tracing for performance monitoring
- CloudWatch metrics for operational insights
- Configurable log group data protection
- AWS Bedrock AgentCore observability for agent-specific insights
AgentCore Observability
AWS Bedrock AgentCore provides agent-specific observability that complements Lambda Powertools by capturing agent-level metrics and traces. When you enable observability on your agent, both systems work together to provide complete visibility into your AI agent's behavior and performance.
What is AgentCore Observability?
AgentCore observability automatically collects and publishes metrics about your agent's behavior and decision-making process:
- Agent Invocations: Number of times the agent is invoked and success/failure rates
- Reasoning Steps: How the agent processes requests and makes decisions
- Tool Usage: Which tools the agent calls, how often, and their success rates
- Token Consumption: Number of tokens used per invocation for cost tracking
- Agent Latency: Time taken for agent operations and tool executions
- Error Rates: Failed invocations categorized by error type
These metrics provide deep insights into agent behavior that go beyond standard Lambda function metrics, helping you understand how your AI agent reasons, which tools it prefers, and where optimization opportunities exist.
How to Enable
AgentCore observability is enabled with the same flag as Lambda Powertools - no additional configuration required:
const agent = new BatchAgent(this, 'MyAgent', {
agentName: 'my-agent',
enableObservability: true, // Enables both Lambda Powertools AND AgentCore
metricServiceName: 'my-service',
metricNamespace: 'MyApp',
agentDefinition: {
bedrockModel: {
useCrossRegionInference: true
},
systemPrompt: new Asset(this, 'SystemPrompt', {
path: './prompts/system_prompt.txt'
}),
tools: [
new Asset(this, 'AnalysisTool', {
path: './tools/analysis.py'
})
]
},
prompt: 'Analyze the provided data and generate insights.',
expectJson: true
});
When enableObservability: true:
- Lambda Powertools provides function-level observability (logs, traces, metrics)
- AgentCore provides agent-level observability (invocations, reasoning, tools, tokens)
- Both systems use the same service name and namespace for correlation
- All configuration happens automatically - no manual setup required
What Gets Configured Automatically
Environment Variables (set automatically by the framework):
AGENT_OBSERVABILITY_ENABLED='true': Enables AgentCore observabilityOTEL_RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTES: Service identification for OpenTelemetry (includes service name and log group)OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_LOGS_HEADERS: Agent identification headers for trace correlationAWS_LAMBDA_EXEC_WRAPPER='/opt/otel-instrument': Enables ADOT wrapper for automatic instrumentation
IAM Permissions (granted automatically to the agent role):
- CloudWatch Logs:
logs:CreateLogGroup,logs:CreateLogStream,logs:PutLogEventsfor trace data - X-Ray:
xray:PutTraceSegments,xray:PutTelemetryRecordsfor distributed tracing
Lambda Layers (added automatically):
- ADOT (AWS Distro for OpenTelemetry) Lambda Layer: Provides OpenTelemetry instrumentation for Python
All of this configuration is handled by the framework when you set enableObservability: true - you don't need to configure anything manually.
Querying Metrics in CloudWatch
AgentCore metrics are published to CloudWatch under your configured namespace. You can query them using CloudWatch Logs Insights:
Agent Invocation Count:
fields @timestamp, @message
| filter @message like /agent_invocation/
| stats count() by bin(5m)
Token Usage Analysis:
fields @timestamp, @message
| filter @message like /token_usage/
| parse @message /tokens_used: (?<tokens>\d+)/
| stats sum(tokens) as total_tokens by bin(1h)
Tool Usage Frequency:
fields @timestamp, @message
| filter @message like /tool_call/
| parse @message /tool_name: "(?<tool>[^"]+)"/
| stats count() by tool
Agent Latency Percentiles:
fields @timestamp, @message
| filter @message like /agent_latency/
| parse @message /latency_ms: (?<latency>\d+)/
| stats avg(latency), pct(latency, 50), pct(latency, 95), pct(latency, 99) by bin(5m)
Error Rate by Type:
fields @timestamp, @message
| filter @message like /agent_error/
| parse @message /error_type: "(?<error_type>[^"]+)"/
| stats count() by error_type
Complementary Observability Systems
Both Lambda Powertools and AgentCore observability work together to provide complete visibility:
| Aspect | Lambda Powertools | AgentCore Observability |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Lambda function execution | Agent reasoning and behavior |
| Logs | Function logs, structured logging | Agent traces, reasoning steps, tool calls |
| Metrics | Function metrics (duration, memory, errors), custom metrics | Agent invocations, token usage, tool usage, reasoning latency |
| Traces | Function execution traces, cold starts | Agent decision-making traces, tool execution flows |
| Use Case | Debug function issues, optimize performance | Understand agent behavior, optimize prompts, track costs |
| Granularity | Request/response level | Agent reasoning step level |
Both systems publish to CloudWatch and use the same service name/namespace, making it easy to correlate function-level and agent-level insights in a single dashboard.
Example: Monitoring Agent Performance
// Enable observability for production monitoring
const fraudDetectionAgent = new BatchAgent(this, 'FraudDetectionAgent', {
agentName: 'fraud-detection',
enableObservability: true,
metricServiceName: 'fraud-detection',
metricNamespace: 'FraudDetection',
agentDefinition: {
bedrockModel: {
useCrossRegionInference: true
},
systemPrompt: new Asset(this, 'SystemPrompt', {
path: './prompts/fraud_detection.txt'
}),
tools: [
new Asset(this, 'RiskAnalysisTool', {
path: './tools/risk_analysis.py'
}),
new Asset(this, 'DatabaseLookupTool', {
path: './tools/database_lookup.py'
})
]
},
prompt: 'Analyze the document for fraud indicators.',
expectJson: true
});
// After deployment, query CloudWatch:
// 1. View Lambda function logs (Lambda Powertools) - function-level insights
// 2. View agent reasoning traces (AgentCore) - agent-level insights
// 3. Correlate by service name: "fraud-detection"
// 4. Track token usage for cost optimization
// 5. Monitor tool usage patterns to optimize agent behavior
Best Practices
- Always enable in production: Observability is crucial for understanding agent behavior, debugging issues, and optimizing costs
- Use consistent naming: Use the same service name and namespace across all agents in an application for easier correlation
- Monitor token usage: Track token consumption to optimize costs and identify inefficient prompts
- Analyze tool usage: Understand which tools are most frequently called to optimize tool implementations and agent prompts
- Set up alarms: Create CloudWatch alarms for high error rates, excessive latency, or unusual token consumption
- Review reasoning traces: Regularly review agent reasoning steps to identify opportunities for prompt optimization
- Correlate metrics: Use the same service name to correlate Lambda Powertools and AgentCore metrics in CloudWatch dashboards
- Track trends over time: Monitor agent behavior trends to identify degradation or improvement in performance
Troubleshooting
Metrics not appearing in CloudWatch?
- Verify
enableObservability: trueis set on your agent - Check that IAM permissions are granted (CloudWatch Logs, X-Ray) - these are added automatically by the framework
- Verify ADOT Lambda Layer is attached to the Lambda function
- Check Lambda function logs for OTEL initialization errors
- Ensure the agent has been invoked at least once (metrics appear after first invocation)
High token consumption?
- Review agent reasoning traces in CloudWatch to identify verbose reasoning steps
- Optimize system prompt to reduce unnecessary reasoning
- Consider caching frequently used tool results to avoid redundant LLM calls
- Check if the agent is making unnecessary tool calls
- Review the
expectJsonsetting - JSON extraction may require additional tokens
Agent latency issues?
- Check tool execution time in traces - slow tools impact overall latency
- Review reasoning step count - excessive reasoning increases latency
- Consider optimizing tool implementations for faster execution
- Check if cross-region inference is enabled for better availability
- Monitor cold start times and consider provisioned concurrency for latency-sensitive applications
Missing trace data?
- Verify X-Ray tracing is enabled (automatic with
enableObservability: true) - Check that the ADOT Lambda Layer is properly attached
- Ensure the Lambda function has X-Ray permissions (granted automatically)
- Review CloudWatch Logs for OTEL exporter errors
Tool usage not tracked?
- Verify tools are properly decorated with
@tooldecorator in Python - Check that tool calls are completing successfully (errors may not be tracked)
- Review agent logs to confirm tools are being invoked
- Ensure tool implementations return structured responses
For more information on AWS Bedrock AgentCore observability, see the AWS documentation.
Network Security
- Optional VPC deployment for network isolation
- Configurable subnet selection for different security zones
- Security group management for controlled access
Example Implementations
Advanced Patterns
Multi-Agent Orchestration
const classificationAgent = new BatchAgent(this, 'ClassificationAgent', {
// Configuration for document classification
});
const processingAgent = new BatchAgent(this, 'ProcessingAgent', {
// Configuration for document processing
});
// Use Step Functions to orchestrate multiple agents
Custom Tool Libraries Organize tools into reusable libraries:
const toolLibrary = [
new Asset(this, 'FileTools', { path: './tools/file_utils.py' }),
new Asset(this, 'DataTools', { path: './tools/data_utils.py' }),
new Asset(this, 'APITools', { path: './tools/api_utils.py' })
];
// Reuse across multiple agents
const agent1 = new BatchAgent(this, 'Agent1', {
agentDefinition: { tools: toolLibrary }
});
Environment-Specific Configuration Configure agents differently per environment:
const isProduction = this.node.tryGetContext('environment') === 'production';
const agent = new BatchAgent(this, 'Agent', {
agentDefinition: {
bedrockModel: {
useCrossRegionInference: isProduction
}
},
enableObservability: isProduction
});


